Introduction to Adenoidid
Adenoidid may not be a term you encounter daily, but understanding it can significantly impact health. These small glands play a crucial role in our immune system, particularly during childhood. Unfortunately, they can also become problematic when enlarged or infected. This blog will explore what adenoidid is all about and how to manage any related issues effectively. Whether you’re curious about the symptoms or seeking treatment options for yourself or your child, we’ve got you covered! Let’s dive deeper into this often-overlooked area of health and wellness.
What are Adenoidid and What Do They Do?
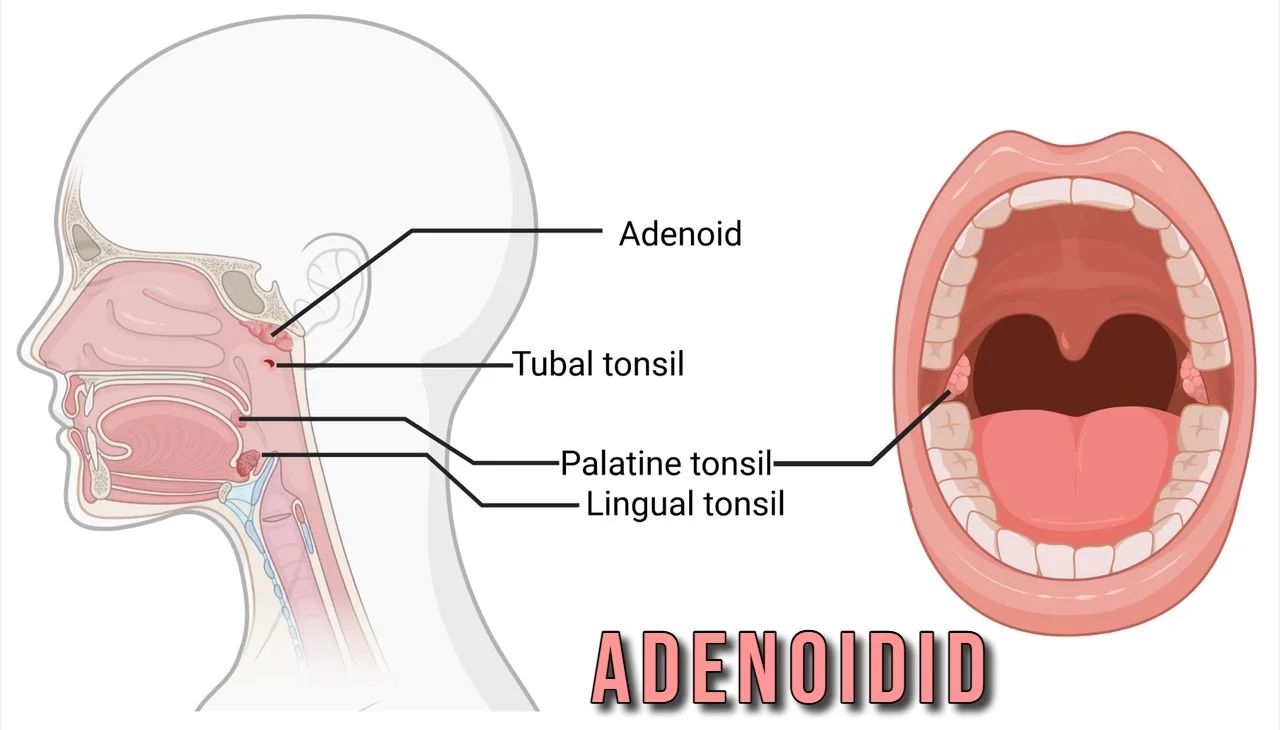
Adenoidid, commonly referred to as adenoids, are small masses of lymphatic tissue located at the back of the nasal cavity. They play a crucial role in our immune system, especially during childhood.
These tissues help trap pathogens entering through the nose and mouth. By doing so, they assist in preventing infections and diseases. Adenoids act like a filter, catching germs before they can reach other parts of the body.
As children grow older, adenoidid tissues often shrink or become less active. This natural process usually occurs by adolescence when their function becomes less critical. However, enlarged adenoids can lead to various health issues if not monitored properly.
Maintaining a healthy set of adenoidid is important for overall well-being in early life stages.
Causes of Adenoidid
Adenoidid can arise from various factors that impact the growth and function of adenoids. One primary cause is recurrent infections, particularly during childhood. Frequent bouts of colds or respiratory illnesses can lead to inflammation.
Genetics also play a role in the development of adenoidid. If there’s a family history of enlarged adenoids, children may be more susceptible.
Allergies are another contributing factor. Allergic reactions can trigger swelling in the nasal passages and throat, resulting in larger than normal adenoids over time.
Environmental irritants like smoke or pollution can exacerbate symptoms as well. Chronic exposure might lead to ongoing issues with these lymphatic tissues.
Age matters too; younger children are more likely to experience problems due to naturally smaller airways and developing immune systems. Understanding these causes aids in prevention and management strategies for those affected by adenoidid.
Symptoms of Adenoidid
Adenoidid can manifest through a range of symptoms that can vary between individuals. Common signs often include nasal congestion, which may make breathing difficult, particularly during sleep.
Many people notice persistent snoring or even sleep apnea due to airway obstruction caused by enlarged adenoids. This condition can disrupt restful nights for both the individual and those nearby.
Frequent ear infections are another red flag associated with adenoidid. The swelling may block the Eustachian tubes, leading to fluid buildup in the ears.
Chronic sore throat is also prevalent among those affected. Constant irritation from post-nasal drip can lead to discomfort and frequent throat clearing.
You might observe changes in speech patterns as well; some children develop a nasal quality when speaking, which could indicate underlying issues linked to their adenoids.
Diagnosis of Adenoidid
Diagnosing adenoidid involves a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional. The process typically begins with a detailed medical history. Your doctor will ask about symptoms, frequency of infections, and any breathing difficulties.
A physical examination often follows. This may include looking inside the throat using a light source to assess the size of the adenoids. In some cases, doctors use an endoscope—a thin tube with a camera—to get a closer look.
Imaging tests like X-rays can also help visualize enlarged adenoids. These images provide additional insight into their size and positioning relative to surrounding structures.
It’s essential that parents share any observations regarding their child’s sleep patterns or snoring habits during this assessment. All these steps together allow for an accurate diagnosis tailored to individual needs.
Treatment Options for Adenoidid
Treatment for adenoidid varies based on the severity of symptoms. For mild cases, observation may be sufficient. Doctors often recommend monitoring the situation as children grow.
When symptoms become disruptive, medication can help alleviate discomfort. Antihistamines and nasal corticosteroids are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and relieve nasal congestion.
In more severe instances, surgical intervention might be necessary. Adenoidectomy is a straightforward procedure where the enlarged adenoids are removed. This operation typically leads to significant improvement in breathing and overall quality of life.
Post-surgery care is crucial for recovery. Hydration and rest are essential during this period, allowing the body to heal properly while minimizing complications.
Consultation with an ear, nose, and throat specialist can provide tailored recommendations based on individual needs. Each case is unique, making professional guidance invaluable for effective management of adenoidid.
Prevention and Management Techniques for Adenoidid
Preventing adenoidid involves fostering a healthy environment for children. Regular handwashing can significantly reduce the spread of infections that contribute to enlargement.
Encouraging a balanced diet rich in vitamins A and C supports immune function. Foods like carrots, oranges, and leafy greens can boost overall health.
Maintaining good air quality at home is vital. Using humidifiers can help keep nasal passages moist, reducing irritation. Avoid exposure to secondhand smoke or pollutants as they can aggravate symptoms.
If your child suffers from allergies, identifying triggers and managing them effectively may decrease the risk of developing adenoid-related issues.
Regular check-ups with an ENT specialist are beneficial for monitoring any changes in size or condition related to adenoids. Staying proactive ensures timely intervention if problems arise.
Conclusion
Adenoidid can significantly impact health and well-being, especially in children. Understanding their role is crucial for parents and caregivers.
While they serve as a part of the immune system, enlarged adenoids can lead to various complications. Recognizing symptoms early on promotes timely intervention.
Treatment may range from watchful waiting to surgical removal, depending on severity. Engaging with healthcare professionals ensures informed decisions tailored to individual needs.
Implementing preventative strategies contributes positively to overall respiratory health. Maintaining hygiene and addressing allergies are vital steps that can make a difference.
Being proactive in managing adenoidid helps pave the way for smoother breathing and better quality of life. Staying informed empowers both patients and families alike in navigating this common yet often overlooked issue.
FAQs
Adenoidid can be a perplexing topic, but understanding its nuances is essential for effective management. Here are some frequently asked questions that shed light on this condition:
What are adenoidid?
Adenoidid refers to the inflammation or enlargement of the adenoids, which are small masses of lymphatic tissue located at the back of your nasal cavity. They play a role in immune function, particularly in young children.
What causes adenoidid?
Several factors contribute to adenoidid. Common causes include recurrent infections like colds and sinusitis, allergies, and environmental irritants such as smoke and pollution.
How do I know if my child has adenoidid?
Symptoms may vary but often include chronic nasal congestion, breathing difficulties during sleep (like snoring), frequent ear infections, and even changes in speech patterns.
Is there a specific age range when adenoidid occurs most frequently?
Yes! Adenoid enlargement typically occurs in children between ages 3 to 7 years old since their immune systems are still developing.
How is adenoidid diagnosed?
Diagnosis usually involves a physical examination by an ENT specialist who might use endoscopy or imaging tests like X-rays to assess the size of the adenoids.
What treatment options exist for managing adenoidid symptoms?
Treatment may range from watchful waiting for mild cases to medications such as antihistamines or steroids. In more severe situations where breathing issues arise, surgical removal (adenoidectomy) might be necessary.
Can lifestyle changes help prevent or manage symptoms associated with adenoidid?
Yes! Keeping your living environment clean by reducing allergens can help manage symptoms effectively. Additionally, practicing good hygiene—like handwashing—can reduce infection rates.
Are there any long-term effects if not treated?
If left untreated over time, significant enlargement could lead to complications such as sleep apnea or chronic ear infections affecting hearing development in children.
By addressing these common queries about adenoidid while sharing insights into its causes and