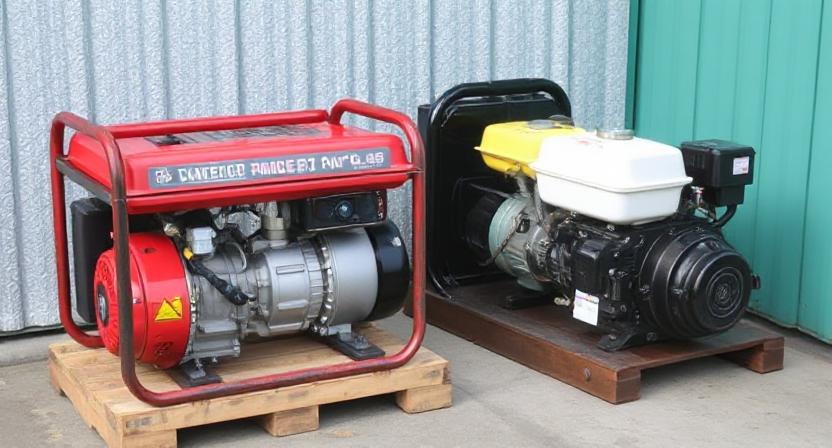
The demand for silent generators has grown steadily over the past few decades, driven by increasing awareness of environmental noise, stricter regulations, and the need for reliable power in settings where peace and quiet are essential. From residential neighbourhoods to outdoor events and from hospitals to remote worksites, the expectation is no longer just about having a dependable source of backup power. Today, it is also about ensuring that generators operate discreetly and harmoniously with their surroundings. As technology continues to advance, the future of silent generators and noise reduction technology looks set to transform the industry.
- The Origins of Noise Reduction in Generators
- The Role of Acoustic Enclosures
- Advances in Muffler and Exhaust Systems
- Engine Design and Noise Reduction
- The Rise of Inverter Generators
- Smart Monitoring and Adaptive Technology
- Hybrid and Renewable-Powered Generators
- Regulations Driving Innovation
- Applications Where Silence Matters Most
- Materials and Acoustic Innovation
- The Future of Urban Generators
- Beyond Silence: A Holistic View of Generator Performance
- Looking Ahead
The Origins of Noise Reduction in Generators
Traditional diesel and petrol generators were notoriously loud. Early designs were focused purely on function, with little attention paid to how much sound they produced. For construction sites and industrial use, this was rarely a concern. Yet as generators became more common in residential and commercial environments, the drawbacks of excessive noise became increasingly apparent.
The first attempts at noise reduction involved enclosing the generator in a basic housing to muffle the sound. While effective to a degree, these enclosures often caused issues with cooling and ventilation, leading to overheating and reduced performance. It quickly became clear that reducing noise was not simply about blocking it but about managing it in ways that complemented the machine’s engineering.
The Role of Acoustic Enclosures
One of the most important innovations in silent generator technology was the development of acoustic enclosures designed specifically to control sound without compromising performance. These enclosures use layers of sound-absorbing materials such as foam and composite insulation to trap noise and reduce the sound that escapes into the environment.
Modern acoustic housings go far beyond basic soundproofing. They are engineered to target specific frequencies, particularly the low-frequency vibrations that are often the most disruptive. They also incorporate clever ventilation designs that allow air to circulate freely, ensuring the generator remains cool without creating additional noise. Over the years, these enclosures have become more compact, lightweight, and durable, making them practical for a wider range of applications.
Advances in Muffler and Exhaust Systems
Another major source of generator noise is the exhaust system. Combustion engines produce significant sound as gases are expelled at high speed and pressure. To tackle this, engineers began adapting muffler technologies similar to those used in vehicles. These mufflers work by redirecting and diffusing exhaust gases through chambers and perforated tubes, reducing the sound before it exits the system.
Recent advancements have made these systems far more effective. Variable-pitch mufflers, catalytic silencers, and advanced materials now enable exhaust systems to reduce noise while also improving emissions performance. This dual benefit is vital, as the future of generator technology is about more than silence—it is also about sustainability and compliance with tightening environmental standards.
Engine Design and Noise Reduction
While enclosures and mufflers play a significant role, the design of the generator’s engine itself is equally important. Early engines were not optimised for quiet operation, but modern designs incorporate features specifically intended to reduce vibration and minimise sound at its source.
High-precision components, better fuel injection systems, and optimised combustion processes now ensure smoother operation and reduced mechanical noise. Vibration dampening mounts and improved bearings further help limit the transmission of sound through the machine’s frame. The result is a generator that is inherently quieter even before external noise reduction measures are applied.
The Rise of Inverter Generators
One of the most significant developments in recent years has been the rise of inverter generators. Unlike traditional generators, which run at a constant speed regardless of load, inverter models adjust their engine speed based on the demand for power. This not only improves fuel efficiency but also dramatically reduces noise during lighter loads.
Inverter generators also produce cleaner electricity, which makes them suitable for powering sensitive equipment such as laptops and medical devices. Their compact size and whisper-quiet operation have made them particularly popular for residential use, camping, and outdoor events. As technology improves, inverter generators are likely to become even quieter, more efficient, and more versatile.
Smart Monitoring and Adaptive Technology
The integration of smart technology into generators has opened new possibilities for noise reduction. Modern control systems can actively monitor performance and adjust operations in real time to minimise noise. For example, an intelligent system might reduce engine speed or modify fuel injection timing to optimise performance while keeping sound levels low.
In the future, machine learning and artificial intelligence could push this further, enabling generators to anticipate noise peaks and adapt accordingly. This type of predictive operation would ensure that generators remain quiet not just by design but also by intelligent, ongoing management of their performance.
Hybrid and Renewable-Powered Generators
One of the most exciting areas of development in silent generator technology is the rise of hybrid systems that combine traditional engines with renewable energy and battery storage. By using stored energy to handle lower loads, the engine can remain idle for long periods, eliminating noise altogether. When the generator is needed, it can run more efficiently by only covering higher loads, reducing both operating time and sound output.
Solar-hybrid generators are already being used in remote locations, construction sites, and events, where noise reduction is a priority. As battery technology improves, these systems will likely become more common, offering a future where generators can provide reliable power with minimal environmental and acoustic impact.
Regulations Driving Innovation
Noise regulations have played a key role in shaping the future of generator technology. In many countries, strict rules limit the acceptable decibel levels for generators used in residential, commercial, or environmentally sensitive areas. The European Union, for example, has set clear standards for permissible noise emissions, and compliance is often a requirement for manufacturers.
These regulations have spurred innovation, pushing manufacturers to invest in research and development to meet increasingly stringent standards. This has led to quieter machines that are not only compliant but also more appealing to customers who value peace and quiet. As regulations continue to evolve, particularly in urban environments, the push for even quieter technology will only intensify.
Applications Where Silence Matters Most
Silent generators are particularly valued in certain environments. In residential neighbourhoods, homeowners need backup power that will not disturb the peace of the community. At outdoor events such as weddings, festivals, and concerts, background noise from a generator can disrupt the experience, making silent models the preferred choice.
Hospitals and healthcare facilities also rely heavily on silent generators. In these settings, the need for reliable backup power is critical, but noise levels must be kept low to avoid disturbing patients. Similarly, hotels, schools, and office buildings prefer silent models to ensure comfort and maintain productivity.
In remote and off-grid environments, silent generators provide power without intruding on natural surroundings, making them suitable for eco-tourism projects and conservation areas. As awareness of noise pollution grows, the demand for silent technology in these applications will continue to expand.
Materials and Acoustic Innovation
One of the most promising areas for future development is the use of advanced materials for sound reduction. Research into lightweight composites, nanomaterials, and innovative insulation technologies is paving the way for enclosures and components that can absorb or deflect sound more effectively than ever before.
For instance, new types of foam insulation with microscopic air pockets can trap sound waves more efficiently, while flexible composite panels reduce vibration transmission. These innovations not only make generators quieter but also lighter and easier to transport, increasing their practicality across multiple sectors.
The Future of Urban Generators
As cities grow denser and reliance on backup power increases, silent generators will play a crucial role in urban environments. The future will likely see compact, ultra-quiet generators integrated into residential and commercial buildings as standard. These units will be designed to blend seamlessly into their surroundings, operating in the background without drawing attention.
Noise reduction in urban areas will go hand in hand with sustainability. Hybrid and fully electric generators powered by batteries or fuel cells may soon replace traditional combustion engines altogether, eliminating noise and emissions simultaneously. The combination of noise-free operation and green energy will align with wider goals to create cleaner, quieter, and more liveable cities.
Beyond Silence: A Holistic View of Generator Performance
While silence is a key focus, the future of generator technology is about more than just reducing decibels. Customers increasingly expect systems that are quiet, efficient, sustainable, and connected. The integration of noise reduction with smart monitoring, renewable energy, and predictive maintenance means that tomorrow’s generators will be more versatile and user-friendly than ever before.
The ongoing shift from noisy, industrial machines to sophisticated, near-silent systems represents a broader transformation in the energy industry. It reflects growing awareness of how technology can adapt to human needs, prioritising not only functionality but also comfort, sustainability, and environmental responsibility.
Looking Ahead
The evolution of silent generators and noise reduction technology is a story of continuous progress driven by necessity, innovation, and regulation. From the early days of crude enclosures to the modern era of smart, hybrid, and renewable-powered systems, the journey has been marked by significant achievements in engineering and design.
The future promises even quieter, more sustainable, and more intelligent generators that can adapt to their environments with minimal human input. Whether through advanced acoustic materials, AI-driven performance optimisation, or complete transitions to battery and renewable systems, silent generator technology is on a path towards becoming the standard rather than the exception.
In a world where power reliability must coexist with environmental consciousness and quality of life, silent generators represent not just a technological advancement but a necessary step forward. They embody the balance between human comfort and industrial capability, ensuring that the energy we rely on does not come at the cost of peace and quiet.