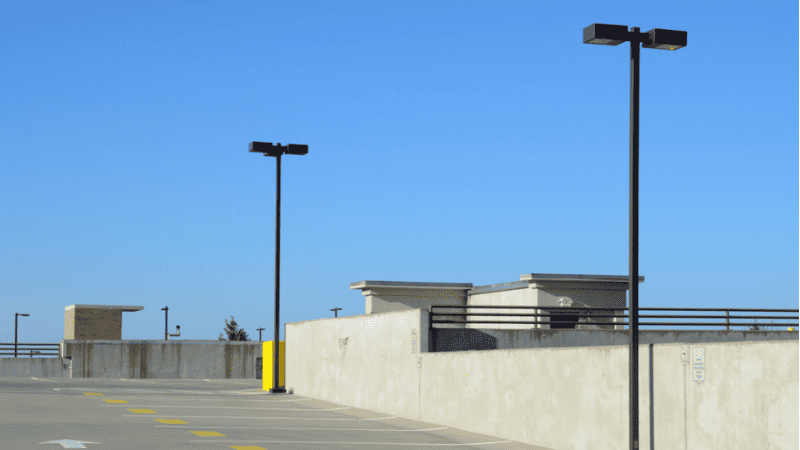
Parking lot light poles are tall structures that hold lights. They range from 12 to 40 feet high. These poles light up large outdoor areas like shopping centers and office buildings.
The poles are made from strong materials. They can handle bad weather like storms and high winds. Each pole has several parts that work together:
- Pole body: Made from aluminum, steel, or fiberglass
- Foundation: Concrete base that keeps the pole stable
- Wiring: Electrical parts hidden inside the pole
- Light fixture: The actual light source at the top
- Controls: Switches and timers that control the lights
Good parking lot lights remove dark spots. They create even lighting across the whole area. This helps people walk and drive safely, notes Lexington Property Management.
Types of Parking Lot Light Poles
Different types of poles work for different needs. Your choice depends on your budget, location, and style preferences.
Straight Pole Design
Straight poles are the most common type. They have a simple design that works almost everywhere. These poles are cost-effective for large parking lots.
Key features:
- Heights from 12 to 40 feet
- Made from aluminum or steel
- Handle winds up to 150 mph
- Easy to install and maintain
- Works with most building styles
Decorative Poles
Decorative poles look better than basic straight poles. They work well for upscale shopping centers and fancy office buildings. These poles cost more but improve the area’s appearance.
Key features:
- Special designs and textures
- Custom colors and finishes
- Usually 12 to 25 feet tall
- Can include planters or signs
- Higher price than basic poles
Hinged Base Poles
Hinged poles can fold down for easy maintenance. Workers can fix the lights without using tall trucks. This saves money and reduces safety risks.
Key features:
- Fold down to ground level
- Safer maintenance work
- Lock in place to prevent tampering
- Cost less to maintain over time
- Need stronger foundations
Materials Used for Light Poles
The material you choose affects how long your poles last. It also changes maintenance costs and appearance.
Aluminum Poles
Aluminum poles resist rust very well. They weigh less than steel poles. This makes them easier to ship and install.
Benefits:
- Never rust or corrode
- Light weight reduces shipping costs
- Last 25 to 50 years
- Can be recycled completely
- Work great near oceans
Drawbacks:
- Cost more upfront
- May need special tools for repairs
Steel Poles
Steel poles are strong and cost less to buy. They work well in most locations. Modern steel poles have special coatings that prevent rust.
Benefits:
- Lower starting cost
- Very strong in high winds
- Easy to find and buy
- Can be repaired in the field
- Available in standard sizes
Drawbacks:
- Can rust without proper coating
- Heavier than aluminum
- May need more maintenance
Fiberglass and Composite Poles
These newer materials resist chemicals and salt water. They work great in harsh environments. They also don’t conduct electricity.
Benefits:
- Resist all chemicals and salt
- Don’t conduct electricity
- Never fade in sunlight
- Need very little maintenance
- Can be made in custom shapes
Drawbacks:
- Higher cost than traditional materials
- Fewer suppliers available
- Limited repair options
Height and Spacing Guidelines
Proper height and spacing create even lighting. This removes dark spots that can hide dangers. Good spacing also saves money by using fewer poles.
Choosing the Right Height
Pole height affects how much area each light covers. Taller poles light larger areas but may create glare.
Height recommendations:
- 12-15 feet: Small lots and walkways
- 20-25 feet: Most retail parking lots
- 30 feet: Large shopping centers
- 40+ feet: Very large areas and sports facilities
Taller poles need stronger foundations. They also cost more to maintain because workers need special equipment to reach them.
Optimal Spacing Between Poles
The space between poles should be 3 to 4 times the pole height. This creates even lighting without dark spots.
Spacing guidelines:
- 20-foot poles: Space 60-80 feet apart
- 25-foot poles: Space 75-100 feet apart
- 30-foot poles: Space 90-120 feet apart
Square or rectangular patterns work best. Place poles closer together near buildings and walkways where people need more light.
Installation and Foundation Requirements
Proper installation keeps poles safe and working for many years. The foundation must handle wind loads and support the pole’s weight.
Foundation Types
Different foundation types work for different situations. The choice depends on soil conditions and pole height.
Concrete foundations:
- Poured concrete footings sized for wind loads
- Depth equals 10% of pole height plus 2 feet
- Must drain water away from the base
- Need to avoid underground utilities
Direct burial:
- Pole goes straight into concrete
- Works for smaller poles
- Faster installation
- Less expensive than separate footings
Electrical Installation
All electrical work must follow safety codes. Licensed electricians should do this work to prevent fires and injuries.
Key requirements:
- Underground cables in conduit or direct burial rated
- Proper grounding systems for safety
- Circuit breakers sized for the load
- Waterproof connections and junction boxes
- Photocells or timers to control operation
LED Technology Benefits
LED lights have changed parking lot lighting. They use less energy and last much longer than old bulb types.
Energy Savings
LED fixtures use 50% to 80% less electricity than old lighting. This cuts power bills significantly.
LED advantages:
- Produce 130-150 lumens per watt
- Old bulbs only produce 80-100 lumens per watt
- Lower electric bills every month
- Utility companies often give rebates
- Reduce peak demand charges
Longer Life and Less Maintenance
LED lights last 50,000 to 100,000 hours. Old bulbs only last 15,000 to 24,000 hours. This means much less maintenance work.
Maintenance benefits:
- Change bulbs much less often
- Fewer service calls needed
- Lower labor costs
- Less spare parts inventory
- Lights dim gradually instead of burning out suddenly
Better Light Quality
LED lights produce cleaner, whiter light. This helps people see colors better and improves security cameras.
Smart Controls and Automation
Smart controls make parking lot lights even more efficient. They adjust lighting based on activity and time of day.
Motion Sensing
Motion sensors detect when people or cars are present. Lights can dim when no one is around and brighten when activity is detected.
Sensor benefits:
- Save energy during quiet hours
- Provide full lighting when needed
- Improve security by responding to movement
- Extend bulb life by reducing operating hours
Wireless Controls
Wireless systems let managers control lights remotely. They can monitor energy use and get alerts when lights need service.
Smart features:
- Control lights from any computer
- Get email alerts for problems
- Track energy usage
- Schedule automatic operation
- Adjust brightness levels remotely
Safety and Security Features
Good lighting prevents crime and accidents. It helps people feel safe in parking areas.
Crime Prevention
Well-lit parking lots discourage criminal activity. Criminals avoid areas where they can be easily seen.
Security benefits:
- Eliminate hiding spots in shadows
- Allow security cameras to work better
- Help people identify faces
- Encourage natural surveillance
- Reduce theft and vandalism
Emergency Features
Some light poles can include emergency call buttons and cameras. These help people get help quickly when needed.
Emergency options:
- Two-way communication systems
- Bright blue emergency lights
- Panic buttons for immediate help
- Camera integration
- GPS location identification
Maintenance and Lifecycle Management
Regular maintenance keeps lights working properly. It also extends their useful life and prevents costly repairs.
Preventive Maintenance
Regular inspections catch problems early. This prevents small issues from becoming expensive repairs.
Maintenance schedule:
- Monthly visual inspections
- Annual electrical testing
- Clean fixtures quarterly
- Check foundations yearly
- Test emergency systems regularly
Long-term Planning
Good planning helps spread out replacement costs. It also allows for technology upgrades over time.
Planning considerations:
- Track pole age and condition
- Budget for future replacements
- Plan LED retrofits for old systems
- Consider smart control upgrades
- Monitor new technology developments
Cost Analysis and Return on Investment
Understanding total costs helps make better decisions. LED systems cost more upfront but save money over time.
Initial Costs
The total project cost includes more than just the poles and lights.
Cost components:
- Poles and fixtures
- Installation labor
- Electrical work
- Permits and inspections
- Site preparation
- Design services
Long-term Savings
Energy savings and reduced maintenance create ongoing value.
Savings sources:
- Lower electricity bills
- Reduced maintenance costs
- Fewer replacement parts
- Utility rebates and incentives
- Insurance premium reductions
- Higher property values
Most LED projects pay for themselves in 3 to 7 years through energy savings alone.
Environmental Impact
Modern parking lot lighting helps protect the environment. LED systems reduce carbon emissions and light pollution.
Carbon Footprint Reduction
LED lights use less electricity from power plants. This reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
Environmental benefits:
- 50-80% reduction in carbon emissions
- Lower stress on electrical grid
- Support for renewable energy
- Reduced manufacturing waste
- Longer product lifecycles
Dark Sky Compliance
Good lighting design prevents light pollution. This protects wildlife and reduces sky glow.
Dark sky features:
- Lights point downward only
- Warm color temperatures
- Automatic dimming at night
- Proper shielding
- Reduced impact on wildlife
Future Trends
Parking lot light poles are becoming smarter and more versatile. They can now do more than just provide lighting.
Electric Vehicle Charging
Many new poles include electric car charging stations. This adds value and attracts environmentally conscious customers.
EV charging benefits:
- Convenient location for charging
- Use existing electrical infrastructure
- Generate additional revenue
- Support sustainability goals
- Meet growing demand
Smart City Integration
Light poles can host various smart city technologies.
Smart features:
- WiFi hotspots
- Air quality sensors
- Traffic monitoring
- Digital signage
- Emergency communications
- 5G cellular equipment
Selecting the Right System
Choosing the best parking lot lighting requires careful planning. Consider your specific needs and long-term goals.
Site Assessment
Evaluate your location’s specific requirements.
Assessment factors:
- Parking lot size and layout
- Current electrical capacity
- Soil conditions
- Wind loads and weather
- Security requirements
- Budget constraints
- Future expansion plans
Technology Selection
Choose the right combination of poles, lights, and controls.
Selection criteria:
- LED efficiency ratings
- Control system capabilities
- Material durability
- Warranty coverage
- Manufacturer reputation
- Installation requirements
Conclusion
Parking lot light poles provide safety and security for any business. LED technology offers better lighting while cutting energy costs. Smart controls add convenience and extra savings.
Quality lighting pays for itself through lower energy bills and reduced maintenance. Modern systems last for decades with proper care. Choose LED technology and work with experienced professionals for the best results.