In the world of modern PCB assembly (PCBA) design, FPGAs (Field-Programmable Gate Arrays) and CPLDs (Complex Programmable Logic Devices) are crucial components that offer flexible solutions for customizing logic circuits. While both devices provide reconfigurable logic, they cater to different needs and have unique features. Understanding the differences between FPGA and CPLD is essential for PCB designers to make informed decisions about which component is best suited for a given project. In this article, we will explore key considerations that designers must take into account when choosing between FPGA and CPLD in modern PCBA design.
- Architecture and Complexity
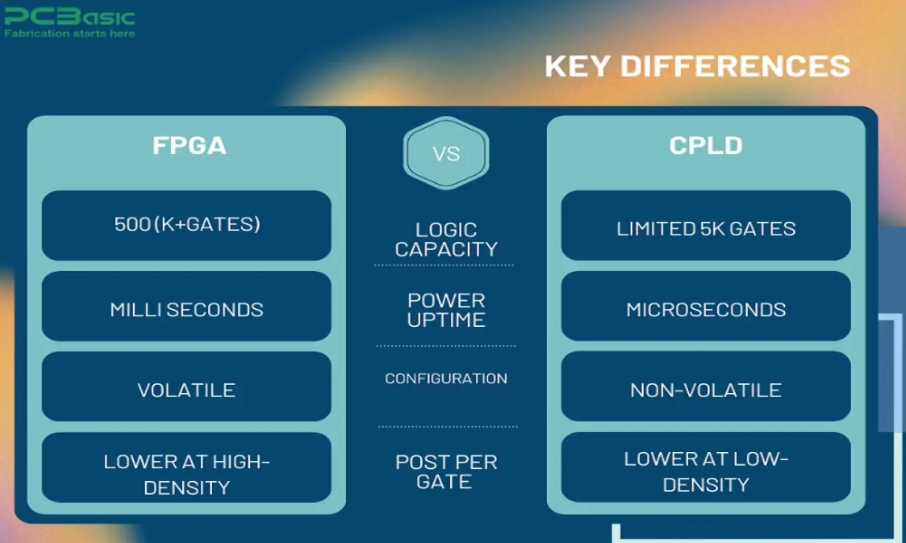
One of the primary differences between FPGA and CPLD is their architecture. FPGAs are generally more complex, featuring a larger number of logic gates and flip-flops, which enables them to handle complex tasks such as high-speed signal processing, video processing, and communication protocols. They consist of a vast array of programmable logic blocks connected by a programmable interconnect network.
In contrast, CPLDs have a simpler architecture. They typically consist of fewer logic gates and are suited for tasks that do not require the level of complexity provided by FPGAs. CPLDs are ideal for implementing smaller logic functions such as glue logic, address decoding, or simple state machines.
- Speed and Performance
When it comes to speed and performance, FPGAs generally outperform CPLDs. FPGAs are capable of handling high-speed data processing and complex algorithms, which makes them ideal for applications like digital signal processing (DSP) and high-frequency communications. Their parallel architecture allows multiple operations to be performed simultaneously, significantly improving overall performance.
On the other hand, CPLDs have a lower maximum operating speed and are better suited for lower-speed, less demanding applications. While CPLDs can still perform well in a variety of scenarios, they may not offer the same performance levels required for high-speed or high-frequency applications found in advanced PCBA designs.
- Power Consumption
Power consumption is another important factor when selecting between FPGA and CPLD for PCBA. FPGAs typically consume more power than CPLDs due to their complex architecture and the large number of logic gates involved. High-performance FPGAs designed for intensive applications often require significant amounts of power, which may be a concern in power-sensitive designs such as portable devices or battery-operated systems.
CPLDs, being simpler and more power-efficient, are often a better choice for low-power applications. Their lower gate count and simplified structure result in reduced power consumption, making them an ideal option for low-cost, low-power PCBA designs.
- Cost Considerations
Cost is always a key consideration in any design. FPGAs, especially high-performance models, tend to be more expensive than CPLDs due to their complexity and capabilities. If your PCBA design requires a high level of logic processing or large-scale custom circuits, the increased cost of an FPGA may be justified. However, if the design only requires simple logic functions or basic control tasks, opting for a CPLD can save on costs without sacrificing functionality.
- Design Flexibility and Development Tools
Both FPGAs and CPLDs offer design flexibility, allowing designers to program and reprogram the devices according to specific needs. However, FPGAs are typically more flexible in terms of functionality, given their larger number of logic blocks and ability to handle complex algorithms and data flows.
The development tools for FPGAs are often more advanced, with support for a wide range of design flows, including hardware description languages (HDLs) such as VHDL or Verilog, and tools like Xilinx ISE or Intel Quartus. CPLD development tools are generally simpler and may offer limited functionality compared to FPGA tools. However, for less complex designs, CPLD tools can provide a more streamlined and cost-effective design process.
- Application Scenarios
When considering FPGA or CPLD for a PCBA design, it’s important to match the component to the specific requirements of the application:
- FPGAs: Best suited for applications requiring high-speed processing, complex algorithms, or high-density logic such as:
- Digital signal processing (DSP)
- Image and video processing
- Communication systems (e.g., 5G, Ethernet)
- High-performance computing
- Custom accelerators for AI or machine learning
- CPLDs: Ideal for applications requiring simpler logic control or interfacing tasks such as:
- Address decoding and glue logic
- Timing control
- State machine design
- Simple protocol conversion
- Low-power, cost-sensitive applications
- Ease of Integration in PCBA
When integrating FPGAs or CPLDs into a PCBA, designers must also consider their impact on the overall design. FPGAs often require more complex PCB layouts due to their high pin count and intricate routing requirements. These devices may also need additional supporting components like voltage regulators or clock management circuits.
CPLDs, with their simpler design, are easier to integrate into a PCBA. They tend to have fewer pins, simpler routing requirements, and may even be used in conjunction with fewer external components, which can help reduce the overall cost and complexity of the PCB design.
Conclusion
The choice between FPGA and CPLD in modern PCBA design depends on several factors, including the complexity of the logic, speed and performance requirements, power consumption, cost, and ease of integration. FPGAs excel in high-performance, complex applications that require massive parallelism and flexibility, while CPLDs are a better fit for simpler logic tasks with lower power consumption and cost constraints. By carefully considering these factors, designers can choose the right solution for their specific PCBA needs, optimizing both the functionality and cost-efficiency of their designs.
In summary, whether you opt for an FPGA or a CPLD, both offer powerful reconfigurable logic solutions—it’s all about selecting the right one for your particular project.