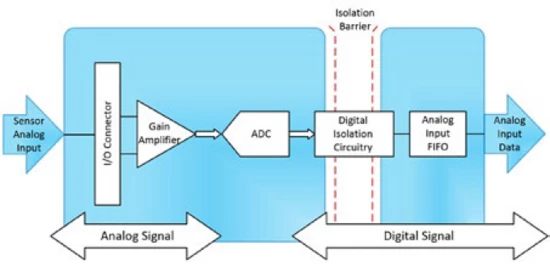
Communication isolation is an important technical means to ensure the normal operation of the communication system in terms of electrical, signal or safety. It isolates the communication signal source from the receiving end by physical or electrical means to prevent interference, noise, voltage shock or safety problems. It is an important means to ensure the safety and reliability of communication equipment. The following introduces several common communication isolation methods.
Opto-Isolation is a technology that uses optical signals to achieve electrical isolation, usually through an optocoupler. An optocoupler consists of a light-emitting diode (LED) and a phototransistor.
Working Principle
When the electrical signal at the input drives the LED to emit light, the optical signal is transmitted to the phototransistor through a transparent insulating medium, turning it on or off, thereby realizing the transmission of the signal. Since the optical signal is not directly connected during the transmission process, it can effectively isolate the electrical systems at the input and output ends.
Advantages
High isolation voltage: Optical isolation can usually withstand a voltage difference of several thousand volts.Strong anti-interference ability: insensitive to electromagnetic interference and noise on site.Fast response speed: usually can reach a communication rate of several M, suitable for high-speed communication scenarios.
Application scenarios
Industrial automation: used to isolate sensor signals and control signals to prevent high-voltage equipment from interfering with the control circuit.
Power system: isolate the communication signals on the high-voltage side and the low-voltage side.Medical equipment: ensure electrical safety between patients and equipment.
Transformer isolation is an isolation method that uses the principle of electromagnetic induction (electricity generates magnetism, magnetism generates electricity) to achieve signal transmission.
Working Principle
The signal generates a magnetic field through the primary coil, and the magnetic field induces the same signal in the secondary coil. Since there is no direct electrical connection between the primary and secondary coils, electrical isolation is achieved. Transformer isolation is usually used for the transmission of analog signals or low-frequency digital signals.
Advantages
High isolation voltage: can withstand high voltage differences.
Good signal integrity: suitable for transmitting analog signals and can maintain signal integrity.
Bidirectional communication: supports bidirectional transmission of signals.
Application scenarios
Audio communication: isolate audio signals to prevent ground loop noise.Industrial communication: isolate low-frequency control signals.Power line communication: isolate communication signals on power lines.
- Capacitive Isolation
Capacitive isolation is an isolation method that uses the coupling effect of capacitors to achieve signal transmission.
Working Principle
Signals are transmitted between two electrically isolated systems through capacitor coupling. The insulating medium of the capacitor can block the passage of DC current, but allows AC signals to pass through, and is usually used for the transmission of digital signals.
Advantages
High isolation voltage: Able to withstand higher voltage differences.Low power consumption: Suitable for low-power applications.Miniaturization: Capacitor isolation devices are usually small in size and suitable for compact designs.
Application scenarios
Medical equipment: Isolate signals between patients and equipment.
Industrial sensors: Isolate sensor signals and control circuits.
Communication interface: Isolate digital communication signals.
- Digital Isolation
Digital isolation is an isolation technology specifically designed for digital signal transmission, which usually combines the advantages of photoelectric isolation or capacitive isolation.
Working Principle
Digital isolators transmit digital signals through photoelectric or capacitive coupling. For example, some digital isolators use micro-LEDs and photodiodes to achieve signal transmission, while others use capacitive coupling technology. Digital isolators have high data transmission rates and low latency.
Advantages
High data rate: suitable for high-speed digital signal transmission.
Low power consumption: suitable for low-power applications.
High reliability: able to work stably in harsh environments.
Application scenarios
High-speed communication interface: isolate USB, SPI, I2C and other communication interfaces.
Industrial automation: isolate digital control signals.
Medical equipment: isolate digital signals to ensure patient safety.
- Isolated Power Supply
Isolated Power Supply is a power supply system that achieves electrical isolation through transformer or switching power supply technology.
Working Principle
The isolated power supply converts the input power supply into an isolated output power supply through a transformer or a switching power supply. There is no direct electrical connection between the input and output, thus achieving electrical isolation. Isolated power supplies are often used to provide safe power supply for communication equipment.
Advantages
High isolation voltage: Able to withstand higher voltage differences.
Low noise: Provides stable power output and reduces the interference of power supply noise on communication signals.
High safety: Prevents power failure from causing harm to equipment and personnel.
Application scenarios
Communication equipment: Provides isolated power supply for communication modules.
Industrial automation: Provides isolated power supply for sensors and controllers.
Medical equipment: Provides safe power supply for medical equipment.
Summary
Communication isolation technology has a wide range of applications in industrial automation, power systems, medical equipment, communication interfaces, etc. Choosing a suitable isolation method requires comprehensive consideration of factors such as specific application requirements, isolation voltage requirements, signal type, and cost.