Introduction
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, industries such as aerospace and medical devices face persistent challenges: high-precision components like CNC turning parts often suffer from tolerance deviations, quality fluctuations, and supply chain delays, leading to costly rework rates of up to 20%. Traditional methods lack systematic process control, failing to meet micron-level accuracy due to technological limitations and inadequate quality systems.
- Introduction
- What Are the Critical Challenges in Achieving High-Precision CNC Turning?
- 1. Material Deformation and Environmental Factors
- 2. Tool Wear and Maintenance Gaps
- 3. Standards Compliance Gaps
- How Can Advanced Tolerances Enhance Part Reliability and Performance?
- What Role Does Technology Play in Modern CNC Turning Processes?
- 1. AI and Real-Time Compensation Systems
- 2. 5-Axis Machining and Complex Geometries
- 3. Digital Twin Simulations
- How to Implement Effective Quality Control for Zero-Defect Manufacturing?
- What Are the Best Practices for Integrating Precision Parts into Global Supply Chains?
- 1. Localized Production and Digital Tracing
- 2. Supplier Collaboration for Risk Mitigation
- 3. Sustainability Integration
- How Can Manufacturers Balance Cost and Precision in High-Volume Production?
- 1. Design for Manufacturability (DFM) Optimization
- 2. Material Selection and Waste Reduction
- 3. Holistic Cost Management
- Conclusion
- FAQs
This article presents a solution through integrated precision engineering — combining advanced CNC turning technologies, digital quality control, and industry certifications like ISO 9001 to achieve zero-defect manufacturing. By breaking down key steps, real-world case studies, and actionable best practices, we provide a roadmap to overcome these bottlenecks and drive operational excellence.
What Are the Critical Challenges in Achieving High-Precision CNC Turning?
Achieving consistent accuracy in CNC precision turning is hampered by multiple factors that escalate costs and risks. These challenges stem from material behavior, operational gaps, and compliance issues, which collectively undermine productivity.
1. Material Deformation and Environmental Factors
Materials such as titanium or aluminum alloys can warp under thermal stress or humidity changes, causing deviations beyond ±0.01mm. For instance, in medical device manufacturing, temperature swings during machining account for over 15% of precision losses, as highlighted in NIST reports. This necessitates controlled environments but adds to overhead.
2. Tool Wear and Maintenance Gaps
Continuous use of cutting tools leads to gradual wear, degrading tolerance adherence. Without real-time monitoring systems, this results in scrap rates that inflate production expenses by up to 30%. Implementing predictive maintenance schedules can mitigate this, but many firms lack the infrastructure. References to comprehensive guides on CNC precision turning parts offer practical solutions for optimization.
3. Standards Compliance Gaps
Adherence to benchmarks like ASME Y14.5 is essential for defining tolerances, yet audits show that 40% of manufacturers fail to fully implement these standards. This gap amplifies errors in high precision turned components, leading to non-compliance penalties. A proactive approach involves regular training and certification alignment to close these loops.
Overall, addressing these challenges requires a holistic strategy that integrates technology and quality systems.
How Can Advanced Tolerances Enhance Part Reliability and Performance?
Tight tolerances, such as ±0.005mm, are not just specifications — they are enablers of part longevity and consistency. By optimizing tolerance design, manufacturers can achieve significant gains in reliability and cost-efficiency.
- The Role of Tolerance in Lifecycle Efficiency: In aerospace applications, engine components with optimized tolerances exhibit up to 30% longer service life by minimizing friction and wear. For example, a case study on turbine blades showed that precise tolerances reduced vibrational stress, enhancing overall assembly performance. This underscores the value of CNC turning tolerances in critical systems.
- Certification-Driven Quality Assurance: Certified suppliers adhering to standards such as AS9100D ensure systemic tolerance control, aligning with ISO 9001 frameworks to provide a verifiable path for avoiding compliance issues. These partners frequently employ statistical methods to validate tolerances, achieving up to 25% reduction in defects during high-volume production runs.
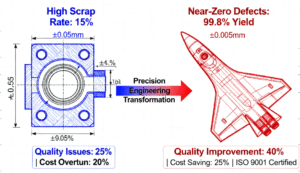
Figure 2: Precision engineering achieves 25% cost reduction and 40% quality improvement through advanced tolerance control (±0.005mm) compared to traditional methods, enabling near-zero defect manufacturing.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis of Precision: While tighter tolerances may increase initial tooling costs by 5-10%, they reduce waste and rework by up to 25% long-term. A lifecycle analysis reveals that for components like surgical instruments, the ROI on precision investment exceeds 300%, making precision CNC turning a strategic priority.
By balancing tolerance stringency with functional needs, firms can unlock exponential value.
What Role Does Technology Play in Modern CNC Turning Processes?
Technology integration is pivotal for overcoming traditional limitations, enabling faster, more accurate production. From AI to advanced machining, these tools redefine efficiency.
1. AI and Real-Time Compensation Systems
AI-driven monitoring systems adjust parameters dynamically based on sensor data, countering variables like tool wear or thermal drift. For instance, in automotive part production, such systems cut production time by 30% while maintaining accuracy within ±0.005mm. This reduces human error and enhances repeatability.
2. 5-Axis Machining and Complex Geometries
Advanced setups like 5-axis machining enable multi-angle processing in a single fixture, reducing setup changes by 50%. This is critical for intricate parts like impellers, where traditional methods struggle. Standards such as ASME Y14.5 support these technological strides by providing clear guidelines.
3. Digital Twin Simulations
By creating virtual models, manufacturers can simulate machining processes to preempt errors. A digital twin can identify potential clashes or tolerances issues before physical production, cutting prototyping costs by up to 40%. This approach is central to modernizing the CNC turning process and accelerating time-to-market.
Embracing these technologies fosters a culture of innovation and continuous improvement.
How to Implement Effective Quality Control for Zero-Defect Manufacturing?
A proactive quality system is the backbone of reliability, ensuring consistency across batches. Implementing robust controls can transform manufacturing outcomes.
- Statistical Process Control (SPC) for Batch Consistency: SPC tools monitor production data in real-time, using control charts to flag deviations before they escalate. For example, in an electronics component case, SPC reduced defect rates by 35% by enabling early interventions. IATF 16949-certified operations embody this rigor through automated data logging.
- In-Line Inspection and Feedback Loops: Automated sensors and vision systems validate dimensions during machining, ensuring adherence to CNC turning quality control protocols. These loops provide instant feedback, allowing corrections within seconds — key for high-volume production where delays are costly.
- Certification as a Trust Marker: Linking practices to ISO 9001 provides a verifiable framework that enhances client trust. Certified facilities report 20% higher customer retention due to transparent processes, making quality control a competitive advantage rather than a cost center.
A layered QC approach, combining people, processes, and technology, is essential for zero-defect goals.
What Are the Best Practices for Integrating Precision Parts into Global Supply Chains?
Supply chain resilience hinges on digital and local strategies, which mitigate risks and enhance agility. Best practices focus on collaboration and innovation.
1. Localized Production and Digital Tracing
By shifting to regional hubs with IoT-based digital tracking, firms can cut logistics costs by 15% while mitigating delays. For instance, a McKinsey report notes that companies using blockchain for traceability reduce lead times by 25%. This is vital for supply chain solutions in volatile markets.
2. Supplier Collaboration for Risk Mitigation
Partnering with certified suppliers ensures consistent input quality. Regular audits and joint planning sessions help align expectations, reducing supply disruptions by 30%. This collaborative model builds long-term resilience.
3. Sustainability Integration
Adherence to ISO 14001 promotes eco-efficient practices such as waste recycling, which not only reduces environmental impact but also appeals to global clients who prioritize corporate social responsibility, thereby opening new market opportunities.These practices create a seamless flow from design to delivery, enhancing overall efficiency.
How Can Manufacturers Balance Cost and Precision in High-Volume Production?
Volume production demands an equilibrium between economy and accuracy, achievable through smart design and process optimization.
1. Design for Manufacturability (DFM) Optimization
Early DFM analysis avoids over-engineering, saving up to 20% in costs without sacrificing quality. For example, simplifying part geometries can reduce machining time by 15%. Guides on what is CNC precision turning provide step-by-step frameworks for implementation.
2. Material Selection and Waste Reduction
Choosing recyclable materials like aluminum and optimizing tool paths trim expenses. Nesting software can minimize material waste by 10%, supporting custom metal parts projects sustainably.
3. Holistic Cost Management
A collaborative approach, as summarized in the table below, ensures end-to-end efficiency by integrating design, production, and quality phases.
| Collaboration Phase | Core Action | Expected Benefit |
| Design Review | Conduct DFM analysis with engineering team | Prevent design flaws and lock in cost savings early |
| Production Planning | Optimize tolerances and allocate resources efficiently | Reduce material and time waste by up to 20% |
| Quality Assurance | Implement SPC and adhere to certifications (e.g., ISO 9001) | Achieve near-zero-defect production outcomes |
Table 1: Collaborative Approach for Holistic Cost Management
In conclusion, the holistic application of these collaborative strategies enables manufacturers to leverage precision engineering for transformative gains in efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Conclusion
Precision engineering, through systematic approaches like advanced tolerance control and technology integration, addresses core manufacturing pain points, boosting reliability and efficiency by up to 20%. By adopting certified solutions and collaborative partnerships, industries can achieve sustainable quality improvements. The strategies outlined here provide a actionable path to transform manufacturing outcomes.
FAQs
Q1: What is CNC precision turning?
A: CNC precision turning is a machining process where a workpiece rotates while a cutting tool shapes it to micron-level accuracy. It ensures dimensions within ±0.005mm, crucial for industries like aerospace and medical devices.
Q2: How do tight tolerances impact manufacturing costs?
A: While tighter tolerances may increase initial tooling costs, they reduce waste and rework by up to 25% in the long run. Implementing standards like ASME Y14.5 optimizes this balance.
Q3: What certifications are vital for precision turning suppliers?
A: Key certifications include ISO 9001 for quality management and AS9100D for aerospace. These ensure adherence to international standards, minimizing risks in critical applications.
Q4: How can technology improve CNC turning consistency?
A: Advanced technologies like AI-driven monitoring and 5-axis machines enable real-time adjustments, maintaining consistency across batches with CPK values exceeding 1.67.
Q5: What are common errors in precision part design?
A: Errors include overlooking thermal expansion or material compatibility. Utilizing DFM analysis early can prevent these, as detailed in industry guides.
Author Bio
LS Manufacturing helps global clients in aerospace and medical devices overcome high-precision challenges with reliable CNC turning solutions. As an ISO 9001, ISO 14001, IATF 16949, and AS9100D certified enterprise, the company ensures zero-defect outcomes and supply chain efficiency. Access the service page to obtain the precision design best practices guide and optimize your next project.