Introduction
As digital services continue to expand across industries, ensuring safe and appropriate access has become a critical responsibility for organizations. From online retail and gaming platforms to healthcare portals and content-driven websites, businesses must confirm that users meet minimum age requirements before granting access. Regulatory pressure, ethical responsibilities, and consumer trust all play a role in driving the adoption of age assurance practices.
This article explores the concept of digital age assurance, why it matters, how it works, and what organizations should consider when implementing it responsibly.
Understanding Age-Based Access Controls
Age-based access controls are mechanisms designed to restrict or permit access to digital products, services, or content based on a user’s age. These controls are particularly relevant for industries dealing with age-restricted goods, sensitive information, or regulated content.
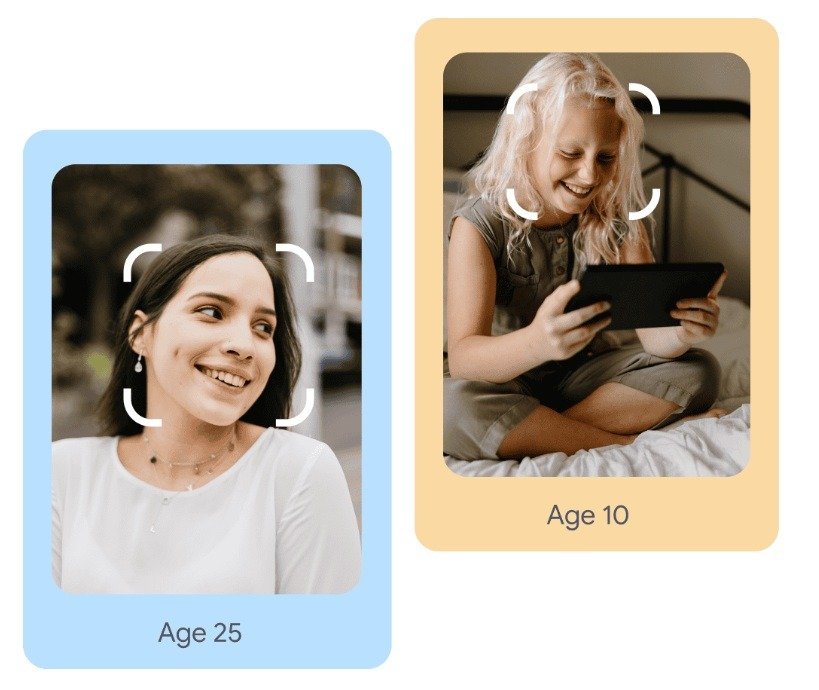
Age Verification plays a central role in this process by enabling organizations to confirm whether a user meets the required age threshold without relying solely on self-declared information. Unlike simple checkboxes or date-of-birth fields, robust age-based controls rely on structured processes that help reduce misuse, protect minors, and support compliance with legal obligations.
At its core, age-based access control is about balancing safety and usability. Effective solutions aim to minimize friction for legitimate users while preventing unauthorized or underage access.
Regulatory and Legal Drivers Behind Age Assurance
Governments and regulatory bodies across the world have introduced laws that require organizations to implement reasonable measures to protect minors online. These regulations often apply to sectors such as digital advertising, social media, online marketplaces, gaming, and adult-oriented services.
Failure to comply can result in substantial fines, reputational damage, and loss of consumer trust. Beyond penalties, regulators increasingly expect businesses to demonstrate proactive risk management and accountability. This means age assurance is no longer optional; it is a compliance requirement in many jurisdictions.
Additionally, data protection laws emphasize user privacy, requiring organizations to confirm age without collecting excessive personal information. As a result, modern age assurance strategies must align with both age-related regulations and broader data protection principles.
Common Methods Used for Age Assurance
There are several approaches organizations use to determine whether a user meets age requirements. Each method has advantages and limitations, depending on the level of assurance needed and the user experience goals.
- Self-declaration: Users enter their date of birth or confirm they meet the age requirement. While simple, this method offers minimal reliability.
- Document-based checks: Users provide official identification to confirm age. This approach offers higher accuracy but requires careful handling of sensitive data.
- Account-based validation: Age is verified once during account creation and reused for future access.
- Attribute-based confirmation: Instead of storing full identity details, systems confirm only whether the age threshold is met.
Organizations often choose a method based on risk level, regulatory requirements, and audience expectations. In many cases, combining methods can improve reliability while maintaining usability.
Privacy and Data Protection Considerations
One of the biggest challenges in age assurance is protecting user privacy. Collecting unnecessary personal data increases risk and can undermine user confidence. Therefore, organizations must adopt privacy-by-design principles when implementing age-related controls.
Key considerations include data minimization, secure storage, and clear retention policies. Users should understand what data is collected, why it is needed, and how long it will be kept. Transparency is essential for maintaining trust.
Modern approaches focus on confirming eligibility rather than identity. By verifying age attributes without storing full personal profiles, organizations can meet compliance requirements while reducing exposure to data breaches and misuse.
Industry Use Cases and Practical Applications
Age assurance is relevant across a wide range of industries. Online retail platforms use it to restrict the sale of regulated products. Media and entertainment services rely on it to manage access to age-appropriate content. Educational platforms apply age controls to protect minors and tailor learning experiences.
Healthcare portals may use age checks to ensure consent rules are followed, while financial services platforms apply age thresholds for account eligibility. In each case, age assurance supports both user safety and organizational responsibility.
As digital ecosystems grow more complex, age assurance becomes a foundational component of trust and governance rather than a standalone feature.
Future Trends in Age Assurance Technology
The future of age assurance is shaped by innovation, regulation, and user expectations. Emerging solutions aim to reduce friction while increasing reliability and privacy protection. Automation, real-time validation, and decentralized approaches are influencing how age-related checks are performed.
Organizations are also placing greater emphasis on inclusivity and accessibility, ensuring that age assurance processes do not exclude users due to technical or documentation barriers. As standards evolve, businesses that adopt flexible and scalable approaches will be better positioned to adapt.
Ultimately, age assurance will continue to shift from a compliance checkbox to a strategic capability that supports safe digital growth.
Conclusion
In today’s digital environment, confirming age is about more than restricting access—it is about building trust, meeting legal obligations, and protecting vulnerable users. As regulations tighten and consumer awareness grows, organizations must adopt thoughtful, privacy-conscious strategies that align with their risk profiles and user needs. By implementing effective Age Verification practices, businesses can create safer online experiences while demonstrating accountability and respect for user privacy.