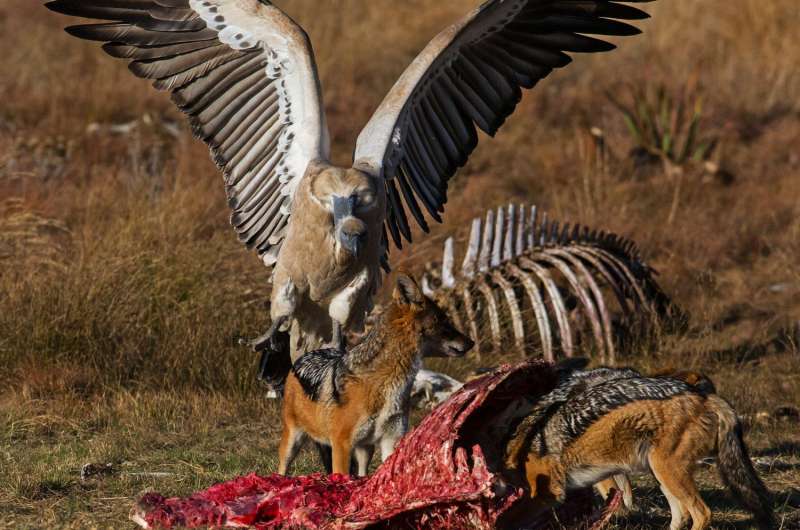
Introduction to fare eaten by scavengers
Nature has a remarkable way of maintaining balance, and scavengers play a vital role in this intricate web. These creatures, often overlooked or misunderstood, feast on the remnants left behind by predators and natural events. The fare eaten by scavengers is not just their sustenance; it represents an essential part of the ecosystem’s recycling process.
- Introduction to fare eaten by scavengers
- The Importance of fare eaten by scavengers in Ecosystems
- Types of Scavengers and Their Characteristics
- Commonly Consumed Fare by fare eaten by scavengers
- Unique Adaptations of Scavengers for Eating
- The Role of Scavengers in Waste Management
- Human-Wildlife Conflict and Solutions for Coexistence with Scavengers
- Conclusion
From vultures soaring high above to insects bustling on the forest floor, each scavenger contributes uniquely to our world. As we dive into this comprehensive guide, you’ll discover how these fascinating animals impact their environment while uncovering what they eat and why it matters so much for all living things. Whether you’re a nature enthusiast or simply curious about wildlife dynamics, there’s something here for everyone!
The Importance of fare eaten by scavengers in Ecosystems
Scavengers play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance. They help break down dead organic matter, recycling nutrients back into the soil. This process enhances soil fertility, promoting plant growth.
By consuming carrion, scavengers prevent the spread of diseases that can arise from decaying remains. Their presence significantly reduces potential health hazards for other wildlife and even humans.
Moreover, they serve as indicators of ecosystem health. A thriving population of scavengers often signifies a balanced environment rich in biodiversity.
In addition to this, scavengers contribute to food webs by providing nourishment for other species. Predators rely on them for sustenance when hunting is scarce or challenging.
Their activities ensure that ecosystems function smoothly and sustainably over time, showcasing nature’s intricate interconnectedness.
Types of Scavengers and Their Characteristics
Scavengers come in various forms, each uniquely adapted to their ecological niche. Birds like vultures dominate the skies, using keen eyesight to spot carcasses from great distances. Their strong beaks help them tear through tough hides.
On land, mammals such as hyenas and jackals thrive on scavenging. Hyenas possess powerful jaws that can crush bones, allowing them access to nutrient-rich marrow. Jackals are more versatile hunters and will often scavenge opportunistically.
Aquatic scavengers also play a crucial role. Species like crabs and certain fish feed on dead marine life, maintaining ocean health by recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem.
Insects cannot be overlooked; beetles are some of the most proficient scavengers on Earth. They consume decaying organic matter quickly, aiding decomposition processes significantly while also serving as food for other animals within their habitats. Each type of scavenger contributes uniquely to environmental balance and nutrient cycling.
Commonly Consumed Fare by fare eaten by scavengers
Scavengers play a crucial role in the ecosystem by consuming a variety of fare. Their diet primarily consists of carrion, which includes dead animals and organic remains that might otherwise go to waste.
These creatures have adapted to locate these food sources efficiently. They often feed on carcasses left behind by predators or those that have succumbed to natural causes.
In addition to animal remains, scavengers also consume fruits and vegetables when available. This diverse diet helps them thrive in various environments, from urban areas to wild landscapes.
Certain species are known for their specific preferences; vultures favor decomposing flesh, while raccoons enjoy rummaging through trash for leftovers. These feeding habits not only sustain scavengers but also contribute significantly to nutrient recycling within ecosystems.
By breaking down organic matter, they facilitate soil enrichment and promote healthy plant growth.
Unique Adaptations of Scavengers for Eating
Scavengers have evolved remarkable adaptations that allow them to thrive on a diet of carrion. Their keen sense of smell is often their greatest asset, enabling them to locate decaying flesh from miles away. Vultures, for example, can detect the scent of rotting animals while soaring high in the sky.
Many scavengers possess specialized beaks and jaws designed for tearing apart tough hides or bones. Hyenas are notable for their powerful jaws that can crush bone, accessing nutrients other animals might miss.
Some species exhibit unique digestive systems capable of handling pathogens found in spoiled meat. This adaptation reduces competition with other carnivores and allows them to consume what others avoid.
Additionally, scavengers often have strong social structures that enhance feeding efficiency. When they work together, they can tackle larger carcasses more effectively than solitary feeders would manage alone. Each characteristic plays a vital role in their survival within diverse ecosystems.
The Role of Scavengers in Waste Management
Scavengers play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance. They act as nature’s cleanup crew, consuming dead animals and organic waste that would otherwise accumulate.
By feeding on carrion, scavengers prevent the spread of diseases. Contaminated carcasses can harbor pathogens that threaten both wildlife and humans. Scavengers help mitigate these risks effortlessly.
Their activities promote nutrient recycling in ecosystems. As they consume decaying matter, they break it down into essential nutrients. This process enriches soil health and supports plant growth.
Additionally, scavenging helps control populations of certain species. By removing deceased individuals from the environment, these creatures ensure a balanced ecosystem where no single species dominates excessively.
Without scavengers, our world would face increased waste accumulation and environmental degradation. Their contributions are often overlooked but are vital for sustainable ecosystems across the globe.
Human-Wildlife Conflict and Solutions for Coexistence with Scavengers
Human-wildlife conflict often arises when scavengers intrude into urban areas. This usually happens in search of food, which can lead to problems for both people and animals.
Cities provide easy access to trash bins and discarded food. Unfortunately, this creates a dangerous cycle where scavengers become reliant on human waste. Such dependence can increase negative interactions.
To promote coexistence, communities need to implement effective waste management practices. Secure trash containers reduce the chances of scavengers raiding neighborhoods for meals. Education is also key; informing residents about natural behaviors helps foster understanding.
Creating wildlife corridors can allow these animals to navigate safely without encroaching on human spaces. Encouraging local biodiversity by preserving natural habitats offers alternative food sources too.
By prioritizing humane solutions and educating the public, we can find ways to share our environment with scavengers harmoniously while minimizing conflicts.
Conclusion
Scavengers play a vital role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems. They thrive on fare that many others might overlook or deem undesirable. By consuming carrion and decaying matter, these creatures help to recycle nutrients back into the environment. This not only supports biodiversity but also ensures healthier habitats.
Understanding the diverse types of scavengers and their unique adaptations offers insight into their importance. From vultures soaring high above to smaller critters like raccoons rummaging through trash cans, each scavenger contributes uniquely to waste management.
However, human activities can sometimes disrupt this balance, leading to conflicts between people and wildlife. Finding effective solutions for coexistence is essential for fostering healthy environments where both humans and scavengers can thrive together.
The next time you encounter an animal feasting on leftover fare, remember its crucial place within the ecosystem’s web of life. Embracing our role in protecting these important creatures will ultimately benefit us all.