Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders can cause jaw pain, headaches, ear discomfort, and difficulty chewing. Understanding which medical and dental specialists are best equipped to diagnose and treat TMJ disorders is crucial for effective care. Early intervention can prevent chronic pain and improve overall quality of life. This article explores the roles of different specialists, treatment options, and practical steps for managing TMJ disorders.
Understanding TMJ Disorders
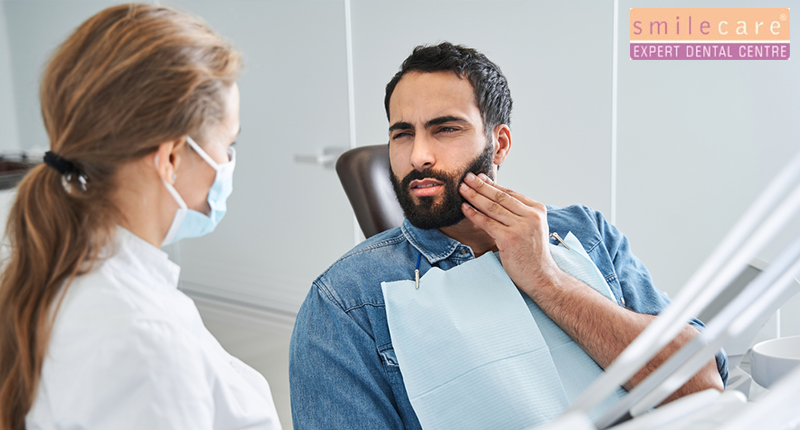
The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) is the hinge that links your jaw to your skull, enabling essential movements like talking, chewing, and yawning. TMJ disorders develop when this joint or the nearby muscles become strained, swollen, or misaligned. Typical signs include pain in the jaw, popping or clicking sounds, difficulty opening or closing the mouth, headaches, and ear discomfort. While TMJ disorders can be caused by trauma, arthritis, or teeth grinding, stress and poor posture often make symptoms worse.
Early diagnosis is important because untreated TMJ disorders can lead to chronic pain, bite problems, and even sleep disturbances. Identifying the right specialist is a critical step toward relief.
Dental Specialists for TMJ Disorders
Dentists and oral and maxillofacial surgeons play a key role in diagnosing and treating TMJ disorders. They focus on structural issues in the jaw and bite, helping patients regain normal function.
Dentists and TMJ Diagnosis
General dentists are often the first point of contact for TMJ concerns. They perform comprehensive oral exams, review medical history, and look for signs of teeth grinding or bite misalignment. Dentists may use imaging tools like X-rays, MRI, or CT scans to assess the joint and surrounding tissues.
TMJ specialists, usually dentists with additional training in occlusion and jaw disorders, can create personalized treatment plans. These plans may include bite splints, orthodontic adjustments, or exercises to relieve tension. Dentists also educate patients on habits that worsen TMJ pain, such as clenching the jaw or chewing hard foods.
Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons
Oral and maxillofacial surgeons are trained to handle more complex TMJ issues, particularly when surgery is needed. Conditions like severe joint damage, chronic dislocation, or degenerative arthritis may require surgical interventions such as arthroscopy or joint replacement. These specialists work closely with dentists and other medical professionals to ensure that surgery is safe and effective.
Medical Specialists for TMJ Disorders
While dental specialists address bite and jaw alignment issues, medical doctors treat TMJ disorders from a broader perspective, focusing on muscle function, inflammation, and overall health.
Ear, Nose, and Throat (ENT) Specialists
ENT specialists evaluate TMJ disorders when patients experience ear pain, tinnitus, or hearing difficulties. Since the TMJ is located close to the ear canal, inflammation in the joint can mimic ear infections or other ENT conditions. ENT doctors help rule out these conditions and may collaborate with dentists to treat TMJ-related symptoms effectively.
Rheumatologists
TMJ disorders linked to autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or lupus require care from rheumatologists. These specialists manage inflammation and prevent joint degeneration using medications, lifestyle adjustments, and monitoring of systemic health. Their expertise ensures that TMJ problems caused by underlying diseases are treated alongside the primary condition.
Physical Therapists
Physical therapists play a crucial role in restoring movement, flexibility, and strength in the jaw and surrounding muscles. They provide exercises to reduce pain, improve posture, and prevent further strain on the TMJ. Physical therapy often complements dental treatments and can reduce the need for surgical interventions.
Pain Management Specialists
Chronic TMJ pain may require intervention from pain management specialists. They use non-surgical options such as nerve blocks, injections, or medication therapy to control discomfort. These doctors often collaborate with dentists, ENT specialists, and physical therapists to provide a comprehensive approach to TMJ care.
Common Diagnostic Approaches
Diagnosing TMJ disorders often requires a combination of clinical evaluation and imaging. Dentists, ENTs, and oral surgeons may use different techniques to confirm the condition.
- X-rays and CT scans help detect bone abnormalities and joint degeneration.
- MRI scans assess soft tissues, including cartilage and muscles.
- Jaw motion analysis measures range of motion, clicking, or locking.
- Patient history and symptom review identify patterns such as teeth grinding or stress-related jaw tension.
Early and accurate diagnosis is key to preventing long-term complications and ensuring effective treatment.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
Most TMJ disorders respond well to non-surgical treatments. These approaches are often the first line of care recommended by dentists and medical specialists.
Bite Splints and Mouthguards
Custom dental splints reduce teeth grinding, alleviate pressure on the joint, and promote proper alignment. These devices are commonly prescribed by dentists and can provide significant pain relief.
Physical Therapy Exercises
Targeted exercises help strengthen jaw muscles, improve flexibility, and reduce tension. Physical therapists may also incorporate posture training and neck stretches to relieve stress on the TMJ.
Medications
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), muscle relaxants, and sometimes corticosteroids help manage pain and inflammation. Doctors and dentists carefully tailor medication plans to minimize side effects and maximize relief.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Simple changes can have a big impact. Reducing stress, avoiding hard foods, practicing jaw relaxation techniques, and maintaining good posture all help manage TMJ symptoms.
Surgical and Advanced Interventions
When conservative treatments fail, surgical options may be considered. These interventions are usually handled by oral and maxillofacial surgeons.
Arthroscopy
A minimally invasive procedure that can remove inflamed tissue or repair minor structural damage.
Open-Joint Surgery
For severe cases, open-joint surgery may reconstruct or replace the TMJ. This is typically a last resort and requires careful coordination between dental and medical specialists.
Joint Replacement
In cases of extreme degeneration, TMJ replacement can restore function and reduce chronic pain. This procedure is highly specialized and involves long-term rehabilitation.
Coordinated Care Approach
TMJ disorders often benefit from a multidisciplinary approach. Patients may see dentists, oral surgeons, ENT specialists, physical therapists, and pain management doctors working together.
Regular communication between specialists ensures:
- Accurate diagnosis of the underlying cause
- Comprehensive treatment addressing jaw alignment, muscle function, and inflammation
- Personalized care plans that reduce pain and improve daily function
This collaborative approach often leads to better outcomes than treatment by a single provider.
When to See a Specialist
It’s important to seek professional care if you experience:
- Persistent jaw pain or stiffness
- Jaw locking or clicking that interferes with chewing
- Frequent headaches or ear pain
- Difficulty opening or closing your mouth
Early consultation with a dentist or medical specialist can prevent symptoms from worsening and may reduce the need for invasive treatments.
Conclusion
Temporomandibular joint disorders can significantly affect daily life, but effective care is available when the right specialists are involved. Dentists, oral and maxillofacial surgeons, ENT specialists, rheumatologists, physical therapists, and pain management doctors all play important roles in diagnosing and treating TMJ disorders.
By combining professional expertise, non-surgical interventions, lifestyle changes, and, when necessary, surgical treatments, patients can find relief and restore jaw function. Early recognition, accurate diagnosis, and coordinated care remain the keys to managing TMJ disorders successfully.
Understanding which specialists to consult ensures that TMJ disorders are treated effectively, helping patients regain comfort, mobility, and overall quality of life.